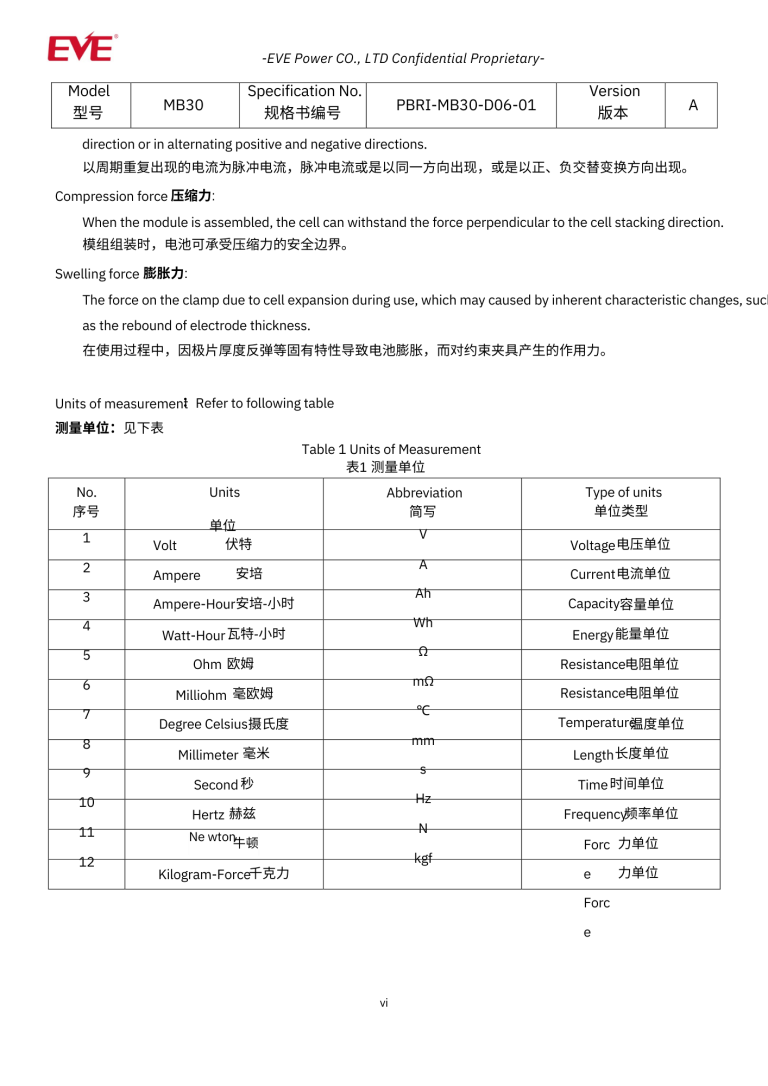
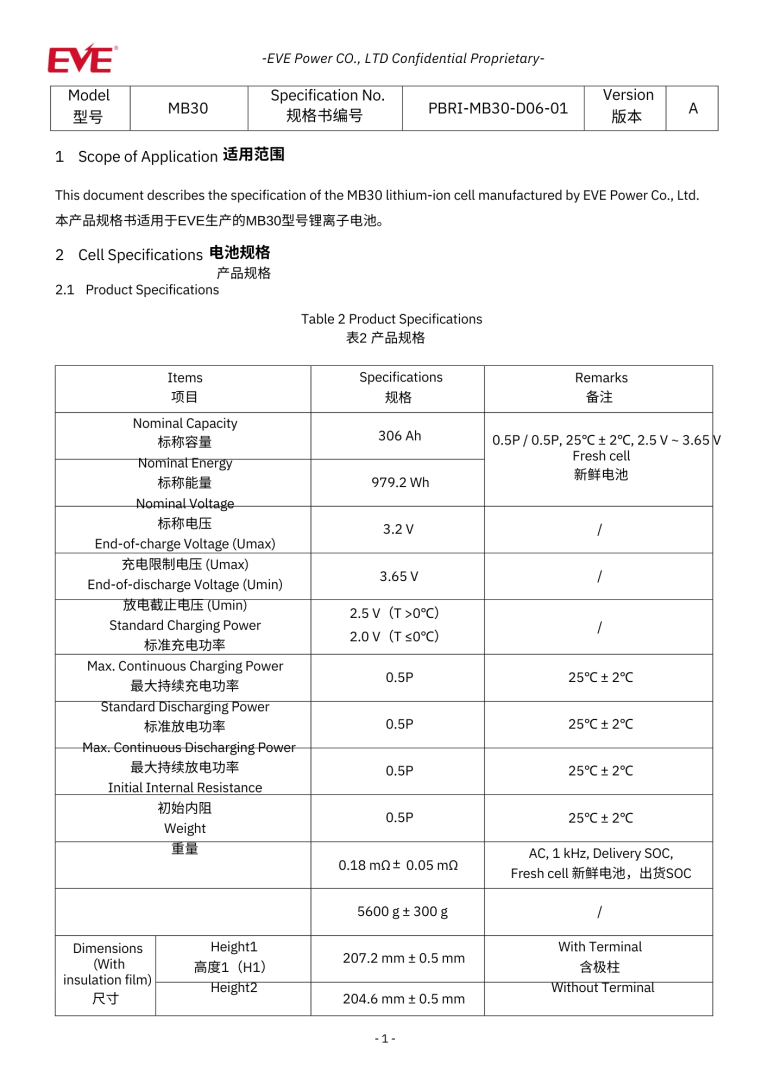
Lithium Phosphate Test Reports































































Lithium phosphate batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery that utilizes lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. This technology is known for its high thermal stability, safety, and long cycle life, making it an ideal choice for various applications, from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage.
These batteries offer several advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries, including a lower risk of thermal runaway, which enhances safety. Additionally, they have a longer lifespan, with some models capable of lasting over 2000 charge cycles, providing excellent value for both consumers and businesses alike.
When evaluating lithium phosphate batteries, several performance metrics are essential, such as energy density, charge/discharge rates, and cycle life. Understanding these metrics helps users make informed decisions regarding battery selection based on their specific needs.
For example, energy density refers to the amount of energy stored per unit of weight, which can significantly affect the range of electric vehicles. Charge/discharge rates determine how quickly a battery can be charged or deliver power, while cycle life indicates the number of complete charge/discharge cycles a battery can undergo before its capacity significantly diminishes.
Safety is a paramount concern in battery technology, and lithium phosphate batteries excel in this area. Their chemical composition results in a lower likelihood of overheating and combustion compared to other lithium-ion batteries, making them a safer option for various applications.
Moreover, many lithium phosphate batteries come equipped with built-in safety mechanisms, such as thermal fuses and battery management systems, which monitor and regulate battery performance to prevent dangerous situations. These features are particularly important in high-demand environments, such as electric vehicles and industrial applications.
Lithium phosphate batteries are increasingly being adopted across diverse sectors due to their reliability and performance. Common applications include electric vehicles, solar energy storage systems, and portable electronic devices, where efficiency and safety are crucial.
For instance, in the automotive industry, these batteries are favored for their longevity and safety, providing a robust power source for electric cars. Additionally, their use in renewable energy systems allows for efficient storage of solar energy, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.